Anti-synthetase syndrome
Updates to Article Attributes
Anti-synthetase syndrome (ASS) is a systemic, inflammatory, autoimmune disease that is characterised by inflammatory myositis, polyarthritis associated with interstitial lung disease (ILD) and anti-synthetase autoantibodies.
It can result from autoantibodies to eight of the aminoacyl-transfer RNA synthetases.
These include
- anti-JO-1: the most common anti-synthetase autoantibody.
- anti PL12:
- anti PL7:
- anti OJ:
- anti EJ:
- anti KS:
- anti ZO:
- anti YRS/tyr:
Radiographic features
Variable dependant on organ involvement
Chest
CT chest
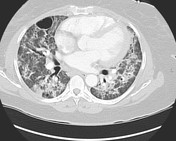
There associated interstitial lung disease may give either a NSIP pattern, a organising pneumonia pattern or a combination 6. The consolidative regions may decrease or resolve in many cases although the disease can at times progress to fibrosis in more than one third of patients .
-<p><strong>Anti-synthetase syndrome (ASS)</strong> is a systemic, inflammatory, autoimmune disease that is characterised by <a href="/articles/inflammatory-myositis">inflammatory myositis</a>, polyarthritis associated with <a href="/articles/interstitial-lung-disease">interstitial lung disease</a> (ILD) and anti-synthetase autoantibodies.</p><p>It can result from autoantibodies to eight of the aminoacyl-transfer RNA synthetases.</p><p>These include</p><ul>- +<p><strong>Anti-synthetase syndrome (ASS)</strong> is a systemic, inflammatory, autoimmune disease that is characterised by <a href="/articles/inflammatory-myositis">inflammatory myositis</a>, <a href="/articles/polyarthritis">polyarthritis</a> associated with <a href="/articles/interstitial-lung-disease">interstitial lung disease</a> (ILD) and anti-synthetase autoantibodies.</p><p>It can result from autoantibodies to eight of the aminoacyl-transfer RNA synthetases.</p><p>These include</p><ul>
-</ul>- +</ul><h4>Radiographic features</h4><p>Variable dependant on organ involvement</p><h5>Chest</h5><h6>CT chest</h6><p>There associated interstitial lung disease may give either a <a title="NSIP" href="/articles/non-specific-interstitial-pneumonia-1">NSIP</a> pattern, a <a title="organising pneumonia" href="/articles/organising-pneumonia">organising pneumonia</a> pattern or a combination<sup> 6</sup>. The consolidative regions may decrease or resolve in many cases although the disease can at times progress to fibrosis in more than one third of patients .</p>
References changed:
- 6. Debray M, Borie R, Revel M et al. Interstitial Lung Disease in Anti-Synthetase Syndrome: Initial and Follow-Up CT Findings. Eur J Radiol. 2015;84(3):516-23. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.11.026">doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.11.026</a> - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25541020">Pubmed</a>
Image 1 CT (lung window) ( update )

Image 2 CT (lung window) ( update )







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.