Burkitt lymphoma
Updates to Article Attributes
Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is an aggressive B-cell lymphoma that predominantly affects children.
Epidemiology
Burkitt lymphoma is the most common (40%) type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in childhood. Median age of Burkitt lymphoma is 8 years and it has a male predominencepredominance (M:F = 4:1) 1. It is less common in adults, accounting for <5% of lymphomas 4.
There isare geographic differences with Burkitt lymphoma considered endemic in parts of Africa and sporadic cases occurring elsewhere.
Risk factors
- HIV infection
- post-transplant immunosuppression
Clinical presentation
BL affects many organs and this affects presentation. Extranodal involvement is common (~30%) at presentation, most often presenting as an abdominal or pelvic mass.
Pathology
Three forms of Burkitt lymphoma have been described 1, 2:
- endemic BL: linked to EBV and Plasmodium falciparum malaria infections
- sporadic BL: aetiology unknown
- immunodeficiency-associated BL
Burkitt lymphoma is an aggressive tumour with a doubling time of 24 hours. It can present in a wide variety of locations:
- head and neck
- pleural space (~70%)
- gastrointestinal tract, especially ileocaecal region
- mesentery, peritoneum, retroperitoneum
- genitourinary tract (~40%)
- gonads (~75%)
Radiographic features
Radiographic features vary widely depending on organ involvement.
Treatment and prognosis
BL can be treated with chemotherapy. In children, prognosis is good with survival rates >90%. In adults, prognosis is poorer, with a 5-year survival rate of ~50% and is even worse with bone marrow or CNS involvement (>30% 5-year survival rate) 4.
History and etymology
It was firstFirst described by Denis Parsons Burkitt, Irish surgeon, in 1958 in equatorialUganda, Africa.
Differential diagnosis
- Crohn's disease may mimic BL on US, barium studies and CT 3
See also
-<p><strong>Burkitt lymphoma</strong> <strong>(BL) </strong>is an aggressive B-cell <a href="/articles/lymphoma">lymphoma</a> that predominantly affects children.</p><h4>Epidemiology</h4><p>Burkitt lymphoma is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in childhood. Median age of Burkitt lymphoma is 8 years and it has a male predominence (M:F = 4:1) 1.</p><p>There is geographic differences with Burkitt lymphoma considered endemic in parts of Africa and sporadic cases occurring elsewhere.</p><h5>Risk factors</h5><ul>- +<p><strong>Burkitt lymphoma</strong> (BL) is an aggressive B-cell <a href="/articles/lymphoma">lymphoma</a> that predominantly affects children.</p><h4>Epidemiology</h4><p>Burkitt lymphoma is the most common (40%) type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in childhood. Median age of Burkitt lymphoma is 8 years and it has a male predominance (M:F = 4:1) <sup>1</sup>. It is less common in adults, accounting for <5% of lymphomas <sup>4</sup>.</p><p>There are geographic differences with Burkitt lymphoma considered endemic in parts of Africa and sporadic cases occurring elsewhere.</p><h5>Risk factors</h5><ul>
-</ul><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>BL affects many organs and this affects presentation. Extranodal involvement is common (~30%) at presentation, most often presenting as an abdominal or pelvic mass.</p><h4>Pathology</h4><p>Three forms of Burkitt lymphoma have been described 1, 2:</p><ul>- +</ul><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>BL affects many organs and this affects presentation. Extranodal involvement is common (~30%) at presentation, most often presenting as an abdominal or pelvic mass.</p><h4>Pathology</h4><p>Three forms of Burkitt lymphoma have been described <sup>1, 2</sup>:</p><ul>
-<li>gastrointestinal tract, mesentery, peritoneum, retroperitoneum</li>-<li>genitourinary tract</li>-<li>gonads</li>-</ul><h4>History and etymology</h4><p>It was first described by <strong>Denis Parsons Burkitt</strong>, Irish surgeon, in 1958 in equatorial Africa.</p><h4>See also</h4><ul>- +<li>pleural space (~70%)</li>
- +<li>gastrointestinal tract, especially ileocaecal region</li>
- +<li>mesentery, peritoneum, retroperitoneum</li>
- +<li>genitourinary tract (~40%)</li>
- +<li>gonads (~75%)</li>
- +</ul><h4>Radiographic features</h4><p>Radiographic features vary widely depending on organ involvement.</p><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><p>BL can be treated with chemotherapy. In children, prognosis is good with survival rates >90%. In adults, prognosis is poorer, with a 5-year survival rate of ~50% and is even worse with bone marrow or CNS involvement (>30% 5-year survival rate) <sup>4</sup>.</p><h4>History and etymology</h4><p>First described by <strong>Denis Parsons Burkitt</strong>, Irish surgeon, in 1958 in Uganda, Africa.</p><h4>Differential diagnosis</h4><ul><li>
- +<a href="/articles/crohn-disease-1">Crohn's disease</a> may mimic BL on US, barium studies and CT <sup>3</sup>
- +</li></ul><h4>See also</h4><ul>
-<a title="lymphoma" href="/articles/lymphoma">lymphoma</a> </li>-<li><a title="WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues" href="/articles/who-classification-of-tumours-of-haematopoietic-and-lymphoid-tissues">WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues</a></li>- +<a href="/articles/lymphoma">lymphoma</a> </li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/who-classification-of-tumours-of-haematopoietic-and-lymphoid-tissues">WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues</a></li>
References changed:
- 3. Seibert JJ, James CA. Pediatric radiology casebase. Thieme. ISBN:0865776970. <a href="http://books.google.com/books?vid=ISBN0865776970">Read it at Google Books</a> - <a href="http://www.amazon.com/gp/product/0865776970">Find it at Amazon</a><span class="auto"></span>
- 4. Diviné M, Casassus P, Koscielny S et-al. Burkitt lymphoma in adults: a prospective study of 72 patients treated with an adapted pediatric LMB protocol. Ann. Oncol. 2005;16 (12): 1928-35. <a href="http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdi403">doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi403</a> - <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16284057">Pubmed citation</a><span class="auto"></span>
Image 1 MRI (T2) ( create )
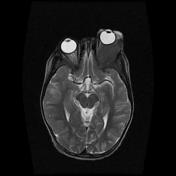
Image 2 X-ray (Frontal) ( create )
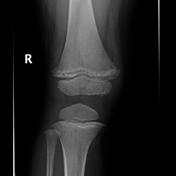
Image 3 CT (C+ portal venous phase) ( create )








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.