Fat stranding (CT)
Updates to Article Attributes
Fat stranding is a common sign on CT seen anywhere fat can be found but is most commonly seen in the abdomen/pelvis, but also in the retroperitoneum, thorax and subcutaneous tissues. It can be helpful in localising both acute and chronic pathology.
Radiographic features
CT
Fat stranding can appear as ill-defined increased attenuation and/or reticular/linear hyperdensity, or in the case of malignancy reticulonodular hyperdensity 1. It is a nonspecific sign in itself and can be seen in infectious, inflammatory, malignant or traumatic conditions.
Abdomen/pelvis
There are several patterns of fat stranding in the abdomen and can occur within the mesentery or surrounding solid organs 1,2:
-
mesenteric fat stranding (misty mesentery)
- bowel and mesenteric trauma
- pericolonic fat stranding with bowel wall thickening
- bowel ischaemia
- colorectal carcinoma
- inflammatory and infectious colitis/enteritis
- pericolonic fat stranding disproportionate to bowel wall thickening
- acute appendicitis
- acute diverticulitis
- epiploic appendagitis: asymmetric on the antimesenteric side
- omental infarction
- sclerosing mesenteritis
- tuberculous peritonitis
- peritoneal malignancy / peritoneal carcinomatosis
- perinephric fat stranding
- peripancreatic fat stranding: acute pancreatitis
- pericholecystic fat stranding: acute cholecystitis
Thorax
Fat stranding can also be seen in thorax, and is mainly indicative of mediastinal pathology:
- mediastinitis
- epipericardial fat necrosis
- traumatic aortic injury
-<p><strong>Fat stranding</strong> is a common sign on CT seen anywhere fat can be found but is most commonly seen in the abdomen/pelvis, but also in the <a href="/articles/retroperitoneum">retroperitoneum</a>, thorax and subcutaneous tissues. It can be helpful in localising both acute and chronic pathology. </p><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>CT</h5><p>Fat stranding can appear as ill-defined increased attenuation and/or reticular/linear hyperdensity, or in the case of malignancy reticulonodular hyperdensity <sup>1</sup>. It is a nonspecific sign in itself and can be seen in infectious, inflammatory, malignant or traumatic conditions. </p><h5>Abdomen/pelvis</h5><p>There are several patterns of fat stranding in the abdomen and can occur within the mesentery or surrounding solid organs <sup>1,2</sup>:</p><ul>- +<p><strong>Fat stranding</strong> is a common sign on CT seen anywhere fat can be found but is most commonly seen in the abdomen/pelvis, but also in the <a href="/articles/retroperitoneum">retroperitoneum</a>, thorax and subcutaneous tissues. It can be helpful in localising both acute and chronic pathology.</p><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>CT</h5><p>Fat stranding can appear as ill-defined increased attenuation and/or reticular/linear hyperdensity, or in the case of malignancy reticulonodular hyperdensity <sup>1</sup>. It is a nonspecific sign in itself and can be seen in infectious, inflammatory, malignant or traumatic conditions.</p><h5>Abdomen/pelvis</h5><p>There are several patterns of fat stranding in the abdomen and can occur within the mesentery or surrounding solid organs <sup>1,2</sup>:</p><ul>
Image 2 CT (renal cortical phase) ( create )

Image 3 CT (non-contrast) ( create )

Image 4 CT (C+ portal venous phase) ( create )

Image 5 CT (non-contrast) ( create )

Image 6 CT (C+ delayed) ( create )

Image 7 CT (C+ portal venous phase) ( create )
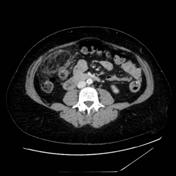
Image 8 CT (C+ portal venous phase) ( create )

Image 9 CT (C+ portal venous phase) ( create )

Image 10 CT (non-contrast) ( create )

Image 11 Annotated image ( create )








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.