Free silicone breast injections
- Integral Diagnostics, Shareholder (ongoing)
- Micro-X Ltd, Shareholder (ongoing)
Updates to Article Attributes
Free silicone breast injections (silicone mastopathy) are an alternative form of breast augmentation to breast implants, although they have serious adverse effects and are banned in many countries.
Radiographic features
There are similar features to that of free silicone from breast implant rupture, although there will be no implant or fibrous capsule.
Mammography
extremely dense lobulated masses +/- rim calcification
extremely dense lymph nodes may be present
Ultrasound
"snowstorm appearance" of echogenic foci with posterior shadowing obscuring the posterior breast 3
MRI
Signal characteristics of silicone:
T1 FS: low signal
T2 water suppressed: high signal
History and etymology
Free silicone injections were the precursor to breast prosthesis implantation and were banned in the United States in the 1990s 1,2. However, they are still performed in developing countries in South America and Asia.
Differential diagnosis
-<p><strong>Free silicone breast injections</strong> (<strong>silicone mastopathy</strong>) are an alternative form of breast augmentation to <a href="/articles/breast-implants">breast implants</a>, although they have serious adverse effects and are banned in many countries. </p><h4>Radiographic features</h4><p>There are similar features to that of free silicone from <a href="/articles/breast-implant-rupture">breast implant rupture</a>, although there will be no implant or fibrous capsule.</p><h5>Mammography</h5><ul>-<li>extremely dense lobulated masses +/- rim calcification</li>-<li>extremely dense lymph nodes may be present</li>-</ul><h5>Ultrasound</h5><ul><li>"snowstorm appearance" of echogenic foci with posterior shadowing obscuring the posterior breast <sup>3</sup>-</li></ul><h5>MRI</h5><p>Signal characteristics of silicone:</p><ul>-<li>-<strong>T1 FS</strong>: low signal</li>-<li>-<strong>T2 water suppressed</strong>: high signal </li>-</ul><h4>History and etymology</h4><p>Free silicone injections were the precursor to breast prosthesis implantation and were banned in the United States in the 1990s <sup>1,2</sup>. However, they are still performed in developing countries in South America and Asia. </p><h4>Differential diagnosis</h4><ul><li>-<a href="/articles/scleroderma">scleroderma</a> <sup>4</sup>-</li></ul>- +<p><strong>Free silicone breast injections</strong> (<strong>silicone mastopathy</strong>) are an alternative form of breast augmentation to <a href="/articles/breast-implants">breast implants</a>, although they have serious adverse effects and are banned in many countries. </p><h4>Radiographic features</h4><p>There are similar features to that of free silicone from <a href="/articles/breast-implant-rupture">breast implant rupture</a>, although there will be no implant or fibrous capsule.</p><h5>Mammography</h5><ul>
- +<li><p>extremely dense lobulated masses +/- rim calcification</p></li>
- +<li><p>extremely dense lymph nodes may be present</p></li>
- +</ul><h5>Ultrasound</h5><ul><li><p>"snowstorm appearance" of echogenic foci with posterior shadowing obscuring the posterior breast <sup>3</sup></p></li></ul><h5>MRI</h5><p>Signal characteristics of silicone:</p><ul>
- +<li><p><strong>T1 FS</strong>: low signal</p></li>
- +<li><p><strong>T2 water suppressed</strong>: high signal </p></li>
- +</ul><h4>History and etymology</h4><p>Free silicone injections were the precursor to breast prosthesis implantation and were banned in the United States in the 1990s <sup>1,2</sup>. However, they are still performed in South America and Asia. </p><h4>Differential diagnosis</h4><ul><li><p><a href="/articles/scleroderma">scleroderma</a> <sup>4</sup></p></li></ul>
References changed:
- 1. Caskey C, Berg W, Hamper U, Sheth S, Chang B, Anderson N. Imaging Spectrum of Extracapsular Silicone: Correlation of US, MR Imaging, Mammographic, and Histopathologic Findings. Radiographics. 1999;19 Spec No(suppl_1):S39-51; quiz S261-2. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1148/radiographics.19.suppl_1.g99oc11s39">doi:10.1148/radiographics.19.suppl_1.g99oc11s39</a> - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10517442">Pubmed</a>
- 2. Venkataraman S, Hines N, Slanetz P. Challenges in Mammography: Part 2, Multimodality Review of Breast Augmentation--Imaging Findings and Complications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(6):W1031-45. <a href="https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.11.7216">doi:10.2214/AJR.11.7216</a> - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22109317">Pubmed</a>
- 3. Leibman A & Misra M. Spectrum of Imaging Findings in the Silicone-Injected Breast. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;128(1):28e-9e. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e31821744d5">doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013e31821744d5</a> - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21701304">Pubmed</a>
- 4. Ralph Weissleder. Primer of Diagnostic Imaging. (2011) ISBN: 9780323065382 - <a href="http://books.google.com/books?vid=ISBN9780323065382">Google Books</a>
- 1. Caskey CI, Berg WA, Hamper UM et-al. Imaging spectrum of extracapsular silicone: correlation of US, MR imaging, mammographic, and histopathologic findings. Radiographics. 1999;19 Spec No (suppl_1): S39-51. <a href="http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/radiographics.19.suppl_1.g99oc11s39">doi:10.1148/radiographics.19.suppl_1.g99oc11s39</a> - <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10517442">Pubmed citation</a><span class="auto"></span>
- 2. Venkataraman S, Hines N, Slanetz PJ. Challenges in mammography: part 2, multimodality review of breast augmentation-imaging findings and complications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197 (6): W1031-45. <a href="http://dx.doi.org/10.2214/AJR.11.7216">doi:10.2214/AJR.11.7216</a> - <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22109317">Pubmed citation</a><span class="auto"></span>
- 3. Leibman AJ, Misra M. Spectrum of imaging findings in the silicone-injected breast. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011;128 (1): 28e-9e. <a href="http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e31821744d5">doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013e31821744d5</a> - <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21701304">Pubmed citation</a><span class="auto"></span>
- 4. Weissleder R, Wittenberg J, Harisinghani MMGH et-al. Primer of Diagnostic Imaging. Mosby. (2011) ISBN:0323065384. <a href="http://books.google.com/books?vid=ISBN0323065384">Read it at Google Books</a> - <a href="http://www.amazon.com/gp/product/0323065384">Find it at Amazon</a><span class="ref_v3"></span>
Image 6 Mammography (LCC pushback) ( destroy )
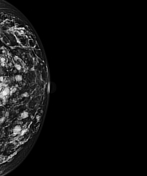
Image 6 Mammography (RCC) ( create )
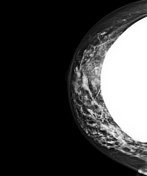
Image 7 Mammography (RCC) ( create )








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.