Hashimoto thyroiditis
- Radiopaedia Events Pty Ltd, Speaker fees (past)
- Integral Diagnostics, Shareholder (ongoing)
- Micro-X Ltd, Shareholder (ongoing)
Updates to Article Attributes
Hashimoto thyroiditis, also known as lymphocytic thyroiditis or chronic autoimmune thyroiditis, is a subtype of autoimmune thyroiditis. It is one of the most common thyroid disorders.
Epidemiology
Typically affects middle-aged females (30-50 year age group with an F:M ratio of 10-15:1).
Clinical presentation
Patients usually present with hypothyroidism +/- goitre. However, a very small proportion of cases (~5%) can present with hyperthyroidism (also known as Hashitoxicosis). There is often a gradual painless enlargement of the thyroid gland during the initial phase with atrophy and fibrosis later on in the course.
The Hashitoxicosis phase, if present, usually only lasts 1-2 months. Although rare cases last much longer 16.
Pathology
There is autoimmunity to the thyroid gland which bears both humoral- and cell-mediated features. This is followed by lymphocytic infiltration of the thyroid gland with lymphoid follicles replacing thyroid follicles. This may affect the thyroid gland in either a diffuse or focal manner. Cell populations include:
lymphocytic aggregates
transformed follicular cells (Askanazy/oxyphilic/Hurthle cells)
Later stages show superadded fibrosis.
Serological markers
antithyroglobulin antibodies: found in ~70% of cases 2
thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPO): found in 90-95% of cases 2
Associations
Hashimoto encephalopathy (rare)
-
other autoimmune disorders
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
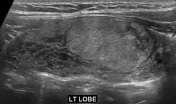
It is difficult to reliably sonographically differentiate Hashimoto thyroiditis from other thyroid pathology. Ultrasound features can be variable depending on the severity and phase of disease 1,5:
diffusely enlarged thyroid gland with a heterogeneous echotexture is a common sonographic presentation (especially initial phase) 6
the glands may be atrophic and small in chronic cases.
the presence of hypoechoic micronodules (1-6 mm) with surrounding echogenic septations is also considered to have a relatively high positive predictive value 3,4; this appearance may be described as pseudonodular or a giraffe pattern
.-
colour Doppler study usually shows normal or decreased flow, but occasionally there might be hypervascularity similar to a thyroid inferno
the hypervascularity does not reflect thyrotoxicosis, indeed it appears to be more common in hypothyroid Hashimoto patients 11
!
prominent reactive cervical nodes may be present, especially in level VI, but they have normal morphologic features
In some situations, large nodules may be present, which may be referred to as nodular Hashimoto thyroiditis 10.
Nuclear medicine
Radioactive iodine
early stages: may show increased uptake
late stages: single or multiple areas of reduced uptake (cold spots)
FDG PET
diffuse high uptake throughout the thyroid is consistent with chronic thyroiditis (or a normal variant) 14,15
superimposed focal high uptake should raise concern for a thyroid nodule including the possibility of carcinoma
History and etymology
It was first described in 1912 by Hakaru Hashimoto (1881-1934), a Japanese physician 7 while working in Germany; in his original description, he called it 'struma lymphomatosa' 13.
Practical points
patients are at higher risk for papillary thyroid carcinoma, so a discrete nodule should be considered for biopsy
Differential diagnosis
For ultrasound appearances consider:
-<p><strong>Hashimoto thyroiditis</strong>, also known as <strong>lymphocytic thyroiditis</strong> or <strong>chronic autoimmune thyroiditis</strong>, is a subtype of <a href="/articles/autoimmune-thyroiditis">autoimmune thyroiditis</a>. It is one of the most common thyroid disorders. </p><h4>Epidemiology</h4><p>Typically affects middle-aged females (30-50 year age group with an F:M ratio of 10-15:1). </p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>Patients usually present with <a href="/articles/hypothyroidism">hypothyroidism</a> +/- <a href="/articles/goitre-2">goitre</a>. However, a very small proportion of cases (~5%) can present with <a href="/articles/hyperthyroidism">hyperthyroidism</a> (also known as Hashitoxicosis). There is often a gradual painless enlargement of the thyroid gland during the initial phase with atrophy and fibrosis later on in the course.</p><p>The Hashitoxicosis phase, if present, usually only lasts 1-2 months. Although rare cases last much longer <sup>16</sup>.</p><h4>Pathology</h4><p>There is autoimmunity to the <a href="/articles/thyroid-gland">thyroid gland</a> which bears both humoral- and cell-mediated features. This is followed by lymphocytic infiltration of the thyroid gland with lymphoid follicles replacing thyroid follicles. This may affect the thyroid gland in either a diffuse or focal manner. Cell populations include:</p><ul>-<li>lymphocytic aggregates</li>-<li>transformed follicular cells (Askanazy/oxyphilic/Hurthle cells)</li>-</ul><p>Later stages show superadded fibrosis.</p><h5>Serological markers</h5><ul>-<li>antithyroglobulin antibodies: found in ~70% of cases <sup>2</sup>-</li>-<li>thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPO): found in 90-95% of cases <sup>2</sup>-</li>-</ul><h5>Associations</h5><ul>-<li><a href="/articles/turner-syndrome">Turner syndrome</a></li>-<li>-<a href="/articles/primary-thyroid-lymphoma">primary thyroid lymphoma </a><sup>6</sup>-</li>-<li>-<a href="/articles/hashimoto-encephalopathy">Hashimoto encephalopathy</a> (rare)</li>-<li><a href="/articles/down-syndrome">Down syndrome</a></li>-<li>other autoimmune disorders <ul>-<li><a href="/articles/systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle">systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/diabetes-mellitus">type 1 diabetes mellitus</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/rheumatoid-arthritis-ra">rheumatoid arthritis</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/sjogren-syndrome-1">Sjogren syndrome</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/primary-biliary-cholangitis">primary biliary cirrhosis</a></li>-</ul>-</li>-</ul><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>Ultrasound</h5><p>It is difficult to reliably sonographically differentiate Hashimoto thyroiditis from other thyroid pathology. Ultrasound features can be variable depending on the severity and phase of disease <sup>1,5</sup>:</p><ul>-<li>diffusely enlarged thyroid gland with a heterogeneous echotexture is a common sonographic presentation (especially initial phase) <sup>6</sup>-</li>-<li>the glands may be atrophic and small in chronic cases.</li>-<li>the presence of hypoechoic micronodules (1-6 mm) with surrounding echogenic septations is also considered to have a relatively high <a href="/articles/positive-predictive-value">positive predictive value</a> <sup>3,4</sup>; this appearance may be described as <a href="/articles/giraffe-pattern">pseudonodular</a> or a <a href="/articles/giraffe-sign">giraffe pattern</a>.</li>-<li>colour Doppler study usually shows normal or decreased flow, but occasionally there might be hypervascularity similar to a <a href="/articles/thyroid-inferno">thyroid inferno</a><ul><li>the hypervascularity does not reflect thyrotoxicosis, indeed it appears to be more common in hypothyroid Hashimoto patients <sup>11</sup>!</li></ul>-</li>-<li>prominent reactive <a href="/articles/cervical-lymph-node-levels">cervical nodes</a> may be present, especially in level VI, but they have normal morphologic features</li>-</ul><p>In some situations, large nodules may be present, which may be referred to as nodular Hashimoto thyroiditis <sup>10</sup>.</p><h5>Nuclear medicine</h5><h6>Radioactive iodine</h6><ul>-<li>early stages: may show increased uptake </li>-<li>late stages: single or multiple areas of reduced uptake (cold spots)</li>-</ul><h6>FDG PET</h6><ul>-<li>diffuse high uptake throughout the thyroid is consistent with chronic thyroiditis (or a normal variant) <sup>14,15</sup>-</li>-<li>superimposed focal high uptake should raise concern for a thyroid nodule including the possibility of carcinoma</li>-</ul><h4>History and etymology</h4><p>It was first described in 1912 by <strong>Hakaru Hashimoto</strong> (1881-1934), a Japanese physician <sup>7 </sup>while working in Germany; in his original description, he called it 'struma lymphomatosa' <sup>13</sup>.</p><h4>Practical points</h4><ul><li>patients are at higher risk for <a href="/articles/papillary-thyroid-cancer">papillary thyroid carcinoma</a>, so a discrete nodule should be considered for biopsy</li></ul><h4>Differential diagnosis</h4><p>For ultrasound appearances consider:</p><ul>-<li><a href="/articles/thyroid-lymphoma">thyroid lymphoma</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/papillary-thyroid-cancer">papillary thyroid carcinoma</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/de-quervain-thyroiditis">subacute granulomatous (de Quervain) thyroiditis</a></li>- +<p><strong>Hashimoto thyroiditis</strong>, also known as <strong>lymphocytic thyroiditis</strong> or <strong>chronic autoimmune thyroiditis</strong>, is a subtype of <a href="/articles/autoimmune-thyroiditis">autoimmune thyroiditis</a>. It is one of the most common thyroid disorders. </p><h4>Epidemiology</h4><p>Typically affects middle-aged females (30-50 year age group with an F:M ratio of 10-15:1). </p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>Patients usually present with <a href="/articles/hypothyroidism">hypothyroidism</a> +/- <a href="/articles/goitre-2">goitre</a>. However, a very small proportion of cases (~5%) can present with <a href="/articles/hyperthyroidism">hyperthyroidism</a> (also known as Hashitoxicosis). There is often a gradual painless enlargement of the thyroid gland during the initial phase with atrophy and fibrosis later on in the course.</p><p>The Hashitoxicosis phase, if present, usually only lasts 1-2 months. Although rare cases last much longer <sup>16</sup>.</p><h4>Pathology</h4><p>There is autoimmunity to the <a href="/articles/thyroid-gland">thyroid gland</a> which bears both humoral- and cell-mediated features. This is followed by lymphocytic infiltration of the thyroid gland with lymphoid follicles replacing thyroid follicles. This may affect the thyroid gland in either a diffuse or focal manner. Cell populations include:</p><ul>
- +<li><p>lymphocytic aggregates</p></li>
- +<li><p>transformed follicular cells (Askanazy/oxyphilic/Hurthle cells)</p></li>
- +</ul><p>Later stages show superadded fibrosis.</p><h5>Serological markers</h5><ul>
- +<li><p>antithyroglobulin antibodies: found in ~70% of cases <sup>2</sup></p></li>
- +<li><p>thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPO): found in 90-95% of cases <sup>2</sup></p></li>
- +</ul><h5>Associations</h5><ul>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/turner-syndrome">Turner syndrome</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/primary-thyroid-lymphoma">primary thyroid lymphoma </a><sup>6</sup></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/hashimoto-encephalopathy">Hashimoto encephalopathy</a> (rare)</p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/down-syndrome">Down syndrome</a></p></li>
- +<li>
- +<p>other autoimmune disorders </p>
- +<ul>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle">systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/diabetes-mellitus">type 1 diabetes mellitus</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/rheumatoid-arthritis-ra">rheumatoid arthritis</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/sjogren-syndrome-1">Sjogren syndrome</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/primary-biliary-cholangitis">primary biliary cirrhosis</a></p></li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
- +</ul><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>Ultrasound</h5><p>It is difficult to reliably sonographically differentiate Hashimoto thyroiditis from other thyroid pathology. Ultrasound features can be variable depending on the severity and phase of disease <sup>1,5</sup>:</p><ul>
- +<li><p>diffusely enlarged thyroid gland with a heterogeneous echotexture is a common sonographic presentation (especially initial phase) <sup>6</sup></p></li>
- +<li><p>the glands may be atrophic and small in chronic cases.</p></li>
- +<li><p>the presence of hypoechoic micronodules (1-6 mm) with surrounding echogenic septations is also considered to have a relatively high <a href="/articles/positive-predictive-value">positive predictive value</a> <sup>3,4</sup>; this appearance may be described as <a href="/articles/giraffe-pattern">pseudonodular</a> or a <a href="/articles/giraffe-sign">giraffe pattern</a></p></li>
- +<li>
- +<p>colour Doppler study usually shows normal or decreased flow, but occasionally there might be hypervascularity similar to a <a href="/articles/thyroid-inferno">thyroid inferno</a></p>
- +<ul><li><p>the hypervascularity does not reflect thyrotoxicosis, indeed it appears to be more common in hypothyroid Hashimoto patients <sup>11</sup></p></li></ul>
- +</li>
- +<li><p>prominent reactive <a href="/articles/cervical-lymph-node-levels">cervical nodes</a> may be present, especially in level VI, but they have normal morphologic features</p></li>
- +</ul><p>In some situations, large nodules may be present, which may be referred to as nodular Hashimoto thyroiditis <sup>10</sup>.</p><h5>Nuclear medicine</h5><h6>Radioactive iodine</h6><ul>
- +<li><p>early stages: may show increased uptake </p></li>
- +<li><p>late stages: single or multiple areas of reduced uptake (cold spots)</p></li>
- +</ul><h6>FDG PET</h6><ul>
- +<li><p>diffuse high uptake throughout the thyroid is consistent with chronic thyroiditis (or a normal variant) <sup>14,15</sup></p></li>
- +<li><p>superimposed focal high uptake should raise concern for a thyroid nodule including the possibility of carcinoma</p></li>
- +</ul><h4>History and etymology</h4><p>It was first described in 1912 by <strong>Hakaru Hashimoto</strong> (1881-1934), a Japanese physician <sup>7 </sup>while working in Germany; in his original description, he called it 'struma lymphomatosa' <sup>13</sup>.</p><h4>Practical points</h4><ul><li><p>patients are at higher risk for <a href="/articles/papillary-thyroid-cancer">papillary thyroid carcinoma</a>, so a discrete nodule should be considered for biopsy</p></li></ul><h4>Differential diagnosis</h4><p>For ultrasound appearances consider:</p><ul>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/thyroid-lymphoma">thyroid lymphoma</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/papillary-thyroid-cancer">papillary thyroid carcinoma</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/de-quervain-thyroiditis">subacute granulomatous (de Quervain) thyroiditis</a></p></li>
Image 1 Pathology (Gross pathology) ( update )

Image 2 Pathology (H&E) ( update )

Image 3 Ultrasound (Longitudinal) ( update )

Image 8 Ultrasound (Longitudinal) ( update )







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.