Intracranial hemorrhage
- Radiopaedia Australia Pty Ltd and Radiopaedia Events Pty Ltd, Director, Founder and CEO (Radiopaedia) (ongoing)
- Biogen Australia Pty Ltd, Investigator-Initiated Research Grant for CAD software in multiple sclerosis: finished Oct 2021 (past)
Updates to Article Attributes
Intracranial haemorrhage (ICH) is a collective term encompassing many different conditions characterised by the extravascular accumulation of blood within different intracranial spaces. A simple categorisation is based on location:
- intra-axial haemorrhage
- extra-axial haemorrhage
Alternatively, intracranial haemorrhage can be thought of in terms of the underlying cause, although in most cases the same aetiology can result in multiple different patterns of haemorrhage.
- trauma
- vascular malformation(s)
- tumour-related haemorrhage
- hypertensive haemorrhage
- cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA)
- cerebral venous thrombosis
Radiographic features
CT
CT scan is almost always the first imaging modality used to assess patients with suspected intracranial haemorrhage. Fortunately, acute blood is markedly hyperdense compared to brain parenchyma, and as such usually poses little difficulty in diagnosis (provided the amount of blood is large enough, and the scan is performed early).
CT angiography (CTA) is increasingly used to assess for a vascular underlying cause, particularly in cases of subarachnoid haemorrhage, or intraparenchymal haemorrhage where something in the presentation, demographics of the patient, or location/appearance of bleed make a primary haemorrhage less likely.
Similarly, CT venogram (CTV) can be used to reliably assess for patency of the dural venous sinuses.
MRI
MRI is typically requested when an underlying abnormality is being sought, particularly when an underlying tumour is suspected. MRI of haemorrhage can pose some challenges in that the appearance of blood changes depending on the sequence and the time since the haemorrhage and the size and location of the bleed.
Angiography
Cerebral angiography is usually performed when a vascular abnormality is suspected and the CT/MR angiogram is either normal (and index of suspicion is high) or equivocal, or in cases where further delineation or treatment of an identified abnormality is required.
-<p><strong>Intracranial haemorrhage</strong> (<strong>ICH</strong>) is a collective term encompassing many different conditions characterised by the extravascular accumulation of blood within different intracranial spaces. A simple categorisation is based on location:</p><ul>-<li>-<strong>intra-axial haemorrhage</strong><ul><li>-<a href="/articles/intracerebral-haemorrhage">intracerebral haemorrhage</a><ul>-<li><a href="/articles/basal-ganglia-haemorrhage-2">basal ganglia haemorrhage</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/lobar-haemorrhage">lobar haemorrhage</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/pontine-haemorrhage">pontine haemorrhage</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/cerebellar-haemorrhage">cerebellar haemorrhage</a></li>-</ul>-</li></ul>-</li>-<li>-<strong>extra-axial haemorrhage</strong><ul>-<li><a href="/articles/extradural-haemorrhage">extradural haemorrhage (EDH)</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/intralaminar-dural-haemorrhage">intralaminar dural haemorrhage</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/subdural-haemorrhage">subdural haemorrhage (SDH)</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/subarachnoid-haemorrhage">subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH)</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/intraventricular-haemorrhage">intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH)</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/subpial-haemorrhage">subpial haemorrhage</a></li>-</ul>-</li>-</ul><p>Alternatively, intracranial haemorrhage can be thought of in terms of the underlying cause, although in most cases the same aetiology can result in multiple different patterns of haemorrhage.</p><ul>-<li>trauma<ul>-<li><a href="/articles/extradural-haemorrhage">extradural haemorrhage (EDH)</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/subdural-haemorrhage">subdural haemorrhage (SDH)</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/subarachnoid-haemorrhage">subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH)</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/cerebral-haemorrhagic-contusion">cerebral haemorrhagic contusion</a></li>-</ul>-</li>-<li>vascular malformation(s)<ul>-<li><a href="/articles/saccular-cerebral-aneurysm">berry aneurysm</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/intracranial-mycotic-aneurysm">mycotic aneurysm</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/arteriovenous-malformation-2">arteriovenous malformation (AVM)</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/dural-arteriovenous-fistula">dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF)</a></li>-</ul>-</li>-<li>tumour-related haemorrhage</li>-<li><a href="/articles/hypertensive-intracerebral-haemorrhage">hypertensive haemorrhage</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/cerebral-amyloid-angiopathy-1">cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA)</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/cerebral-venous-thrombosis">cerebral venous thrombosis</a></li>- +<p><strong>Intracranial haemorrhage</strong> (<strong>ICH</strong>) is a collective term encompassing many different conditions characterised by the extravascular accumulation of blood within different intracranial spaces. A simple categorisation is based on location:</p><ul>
- +<li>
- +<strong>intra-axial haemorrhage</strong><ul><li>
- +<a href="/articles/intracerebral-haemorrhage">intracerebral haemorrhage</a><ul>
- +<li><a href="/articles/basal-ganglia-haemorrhage-2">basal ganglia haemorrhage</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/lobar-haemorrhage">lobar haemorrhage</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/pontine-haemorrhage">pontine haemorrhage</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/cerebellar-haemorrhage">cerebellar haemorrhage</a></li>
- +</ul>
- +</li></ul>
- +</li>
- +<li>
- +<strong>extra-axial haemorrhage</strong><ul>
- +<li><a href="/articles/extradural-haemorrhage">extradural haemorrhage (EDH)</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/intralaminar-dural-haemorrhage">intralaminar dural haemorrhage</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/subdural-haemorrhage">subdural haemorrhage (SDH)</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/subarachnoid-haemorrhage">subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH)</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/intraventricular-haemorrhage">intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH)</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/subpial-haemorrhage">subpial haemorrhage</a></li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
- +</ul><p>Alternatively, intracranial haemorrhage can be thought of in terms of the underlying cause, although in most cases the same aetiology can result in multiple different patterns of haemorrhage.</p><ul>
- +<li>trauma<ul>
- +<li><a href="/articles/extradural-haemorrhage">extradural haemorrhage (EDH)</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/subdural-haemorrhage">subdural haemorrhage (SDH)</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/subarachnoid-haemorrhage">subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH)</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/cerebral-haemorrhagic-contusion">cerebral haemorrhagic contusion</a></li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
- +<li>vascular malformation(s)<ul>
- +<li><a href="/articles/saccular-cerebral-aneurysm">berry aneurysm</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/intracranial-mycotic-aneurysm">mycotic aneurysm</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/arteriovenous-malformation-2">arteriovenous malformation (AVM)</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/dural-arteriovenous-fistula">dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF)</a></li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
- +<li>tumour-related haemorrhage</li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/hypertensive-intracerebral-haemorrhage">hypertensive haemorrhage</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/cerebral-amyloid-angiopathy-1">cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA)</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/cerebral-venous-thrombosis">cerebral venous thrombosis</a></li>
Image ( destroy )
Image 2 Diagram ( create )

Image 3 CT (non-contrast) ( update )

Image 4 CT (non-contrast) ( update )
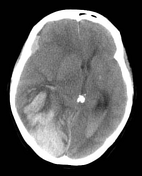
Image 5 CT (non-contrast) ( update )

Image 6 CT (non-contrast) ( update )

Image 7 CT (non-contrast) ( update )

Image 8 CT (non-contrast) ( update )

Image 9 CT (non-contrast) ( update )

Image 10 CT (non-contrast) ( update )

Image 11 CT (non-contrast) ( update )








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.