Paradoxical brain herniation
Updates to Article Attributes
Paradoxical brain herniation is a rare and potentially fatal entity complicating decompressive craniectomy.
Pathology
Atmospheric pressure exceeding intracranial pressure at the craniectomy results in displacement of the brain across various intracranial boundaries. This may result in subfalcine and/or transtentorial herniation. It is often triggered by acute imbalance caused by CSF drainage or lumbar puncture.
Clinical presentation
mayMay range from asymptomatic or mono symptomatic state to acute neurological deterioration.
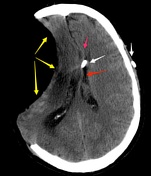
Radiographics
CT or MR
willWill depict large craniectomy and marked concavity of the affected hemisphere with possible associated above mentioned herniations.
Treatment and prognosis
This emergency necessitates immediate intervention to prevent permanent damage:
-
placePlace patient in Trendelenburg position to correct the improper balance between atmospheric and intracranial pressure. -
nextNext steps aim at the correction of the underlying cause e.g. manipulating CSF drains, lumbar puncture sites, consider cranioplasty.
-<p><strong>Paradoxical brain herniation </strong>is a rare and potentially fatal entity complicating decompressive craniectomy. </p><h4>Pathology</h4><p>Atmospheric pressure exceeding intracranial pressure at the craniectomy results in displacement of the brain across various intracranial boundaries. This may result in subfalcine and/or transtentorial herniation. It is often triggered by acute imbalance caused by CSF drainage or lumbar puncture.</p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>may range from asymptomatic or mono symptomatic state to acute neurological deterioration.</p><h4>Radiographics</h4><h5>CT or MR</h5><p>will depict large craniectomy and marked concavity of the affected hemisphere with possible associated above mentioned herniations.</p><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><p>This emergency necessitates immediate intervention to prevent permanent damage: </p><ol>-<li>place patient in Trendelenburg position to correct the improper balance between atmospheric and intracranial pressure.</li>-<li>next steps aim at the correction of the underlying cause e.g. manipulating CSF drains, lumbar puncture sites, consider cranioplasty.</li>- +<p><strong>Paradoxical brain herniation </strong>is a rare and potentially fatal entity complicating decompressive craniectomy. </p><h4>Pathology</h4><p>Atmospheric pressure exceeding intracranial pressure at the craniectomy results in displacement of the brain across various intracranial boundaries. This may result in <a title="Subfalcine herniation" href="/articles/subfalcine-herniation">subfalcine</a> and/or <a title="Transtentorial herniation" href="/articles/transtentorial-herniation">transtentorial herniation</a>. It is often triggered by acute imbalance caused by CSF drainage or lumbar puncture.</p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>May range from asymptomatic or mono symptomatic state to acute neurological deterioration.</p><h4>Radiographics</h4><h5>CT or MR</h5><p>Will depict large craniectomy and marked concavity of the affected hemisphere with possible associated above mentioned herniations.</p><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><p>This emergency necessitates immediate intervention to prevent permanent damage: </p><ol>
- +<li>Place patient in Trendelenburg position to correct the improper balance between atmospheric and intracranial pressure.</li>
- +<li>Next steps aim at the correction of the underlying cause e.g. manipulating CSF drains, lumbar puncture sites, consider cranioplasty.</li>
Image 1 Annotated image (axial NECT obtained in acute setting in a center for neurorehabilitation) ( create )






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.