Sternohyoid muscle
Updates to Article Attributes
The sternohyoid muscle is an infrahyoid muscle of the neck that is innervated by the ansa cervicalis of the cervical plexus receiving fibres from the ventral rami of C1-C3 spinal nerves. The sternohyoid is a paired, flat strap of muscle that serves to fix the hyoid bone as well as depressing the larynx in phonation and in the terminal phase of swallowing.
Summary
- origin: posterior surface of manubrium sterni and the sternoclavicular joint
- insertion: lower body of the hyoid bone
- innervation: anterior rami of C1-C3 spinal nerves through the ansa cervicalis of the cervical plexus
-
action:
- depresses and fixes the hyoid bone
- draws the hyoid bone and underlying larynx downwards in phonation and the terminal phase of swallowing
Gross anatomy
Origin
The sternohyoid muscles are paired muscles that originate from the upper posterior surface of the manubrium and sternoclavicular joints.
Insertion
The muscles travel vertically to insert on the lower border of the hyoid bone. At their insertion on the hyoid bone the sternohyoid muscles lie edge-to-edge however diverge around the laryngeal prominence (Adam’s apple), which protrudes between them.
Relations
The sternohyoid muscle is onone of the infrahyoid “strap” muscles. It is superficial to the sternothyroid and thyrohyoid muscles and inserts just medially to the superior belly of the omohyoid bone on the inferior border of the hyoid bone.
Blood supply
The sternohyoid muscle receives its blood supply from the lingual and superior thyroid arteries.
Nerve supply
The sternohyoid muscles are innervated by the anterior rami of C1 – C3 (predominantly C2 and C3) through the ansa cervicalis of the cervical plexus.
Action
The sternohyoid muscle primarily depresses and fixes the hyoid bone and underlying larynx. Electromyographic studies have also demonstrated the muscle is involved in phonation by depressing the hyoid bone and underlying larynx.
-<![endif]--><!--StartFragment-->The <strong>sternohyoid muscle </strong>is an infrahyoid muscle of the neck that is innervated by the <a href="/articles/ansa-cervicalis">ansa cervicalis</a> of the <a href="/articles/cervical-plexus">cervical plexus</a> receiving fibres from the ventral rami of C1-C3 spinal nerves. The sternohyoid is a paired, flat strap of muscle that serves to fix the hyoid bone as well as depressing the<a href="/articles/larynx"> larynx</a> in phonation and in the terminal phase of swallowing.</p><h4>Summary</h4><ul>- +<![endif]--><!--StartFragment-->The <strong>sternohyoid muscle </strong>is an <a title="Infrahyoid muscles" href="/articles/infrahyoid-muscles">infrahyoid muscle</a> of the neck that is innervated by the <a href="/articles/ansa-cervicalis">ansa cervicalis</a> of the <a href="/articles/cervical-plexus">cervical plexus</a> receiving fibres from the ventral rami of C1-C3 spinal nerves. The sternohyoid is a paired, flat strap of muscle that serves to fix the hyoid bone as well as depressing the<a href="/articles/larynx"> larynx</a> in phonation and in the terminal phase of swallowing.</p><h4>Summary</h4><ul>
-<strong>insertion: </strong>lower body of the hyoid bone</li>- +<strong>insertion: </strong>lower body of the <a href="/articles/hyoid">hyoid</a> bone</li>
-<strong>innervation: </strong>anterior rami of C1-C3 spinal nerves through the ansa cervicalis</li>- +<strong>innervation: </strong>anterior rami of C1-C3 spinal nerves through the <a href="/articles/ansa-cervicalis">ansa cervicalis</a> of the <a href="/articles/cervical-plexus">cervical plexus</a>
- +</li>
-</ul><h4>Gross anatomy</h4><h5>Origin</h5><p>The sternohyoid muscles are paired muscles that originate from the upper posterior surface of the <a href="/articles/manubrium">manubrium</a> and sternoclavicular joints.</p><h5>Insertion</h5><p>The muscles travel vertically to insert on the lower border of the hyoid bone. At their insertion on the hyoid bone the sternohyoid muscles lie edge-to-edge however diverge around the <a href="/articles/laryngeal-prominence">laryngeal prominence</a> (Adam’s apple), which protrudes between them.</p><h5>Relations</h5><p>The sternohyoid muscle is on of the infrahyoid “strap” muscles. It is superficial to the <a href="/articles/sternothyroid-muscle">sternothyroid</a> and <a href="/articles/thyrohyoid-muscle">thyrohyoid</a> muscles and inserts just medially to the superior belly of the omohyoid bone on the inferior border of the hyoid bone.</p><h5>Blood supply</h5><p>The sternohyoid muscle receives its blood supply from the <a href="/articles/lingual-artery">lingual</a> and <a href="/articles/superior-thyroid-artery">superior thyroid arteries</a>.</p><h5>Nerve supply</h5><p>The sternohyoid muscles are innervated by the anterior rami of C1 – C3 (predominantly C2 and C3) through the ansa cervicalis of the cervical plexus.</p><h4>Action</h4><p>The sternohyoid muscle primarily depresses and fixes the hyoid bone and underlying larynx. Electromyographic studies have also demonstrated the muscle is involved in phonation by depressing the hyoid bone and underlying larynx.</p><p> </p><p><!--EndFragment--></p>- +</ul><h4>Gross anatomy</h4><h5>Origin</h5><p>The sternohyoid muscles are paired muscles that originate from the upper posterior surface of the <a href="/articles/manubrium">manubrium</a> and sternoclavicular joints.</p><h5>Insertion</h5><p>The muscles travel vertically to insert on the lower border of the <a href="/articles/hyoid">hyoid</a> bone. At their insertion on the hyoid bone the sternohyoid muscles lie edge-to-edge however diverge around the <a href="/articles/laryngeal-prominence">laryngeal prominence</a> (Adam’s apple), which protrudes between them.</p><h5>Relations</h5><p>The sternohyoid muscle is one of the infrahyoid “strap” muscles. It is superficial to the <a href="/articles/sternothyroid-muscle">sternothyroid</a> and <a href="/articles/thyrohyoid-muscle">thyrohyoid</a> muscles and inserts just medially to the superior belly of the omohyoid bone on the inferior border of the <a href="/articles/hyoid">hyoid</a> bone.</p><h5>Blood supply</h5><p>The sternohyoid muscle receives its blood supply from the <a href="/articles/lingual-artery">lingual</a> and <a href="/articles/superior-thyroid-artery">superior thyroid arteries</a>.</p><h5>Nerve supply</h5><p>The sternohyoid muscles are innervated by the anterior rami of C1 – C3 (predominantly C2 and C3) through the ansa cervicalis of the cervical plexus.</p><h4>Action</h4><p>The sternohyoid muscle primarily depresses and fixes the hyoid bone and underlying larynx. Electromyographic studies have also demonstrated the muscle is involved in phonation by depressing the hyoid bone and underlying larynx.</p><p> </p><p><!--EndFragment--></p>
Image 1 Diagram (Nerve to sternohyoid) ( create )
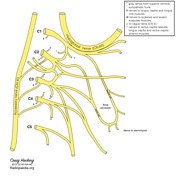
Image 2 Diagram (Cervical plexus labelled) ( create )








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.