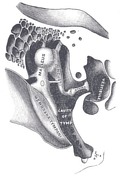
Tympanic membrane
Updates to Article Attributes
The tympanic membrane is a thin membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. It acts to transmit sound waves from air in the external auditory canal to the ossicles of the middle ear.
The malleus is the first bone in the ossicular chain that eventually sees the sound wave transmitted to the oval window of the cochlea.
AnatomyGross anatomy
The tympanic membrane is shaped like a flat cone pointing into the middle and inner ear. It consists of three layers:
- cutaneum (skin)
- radiatum circulare (collagen fibres)
- mucosum (epithelium)
There are two distinct portions to the membrane:
- pars tensa: the tense portion of the membrane is the larger portion and extends from the anterior and posterior malleolar folds at the level of the lateral process of malleus to the inferior edge of the membrane
- pars flaccida: the flaccid portion of the membrane is much smaller and is the portion of the membrane above the anterior and posterior malleolar folds
Quadrant separation
It is anatomically separated into four quadrants:
- anterosuperior
- anteroinferior
- posteroinferior
- posterosuperior
This is important because vessels and nerves (specifically chorda tympani nerve) pass through the superior portion of the membrane. Additionally, the light reflex (cone of light) is specific to the anteroinferior portion of the membrane. Thus, when intervention is performed, the posteroinferior portion of the membrane is chosen.
Related pathology
- conductive hearing loss: secondary to rupture or perforation
- tympanic membrane retraction
-<p>The <strong>tympanic membrane</strong> is a thin membrane that separates the <a href="/articles/external_ear">external ear</a> from the <a href="/articles/middle-ear">middle ear</a>. It acts to transmit sound waves from air in the <a href="/articles/external-auditory-canal">external auditory canal</a> to the <a href="/articles/middle-ear-ossicles">ossicles</a> of the middle ear.</p><p>The <a href="/articles/malleus">malleus</a> is the first bone in the <a href="/articles/ossicular-chain">ossicular chain</a> that eventually sees the sound wave transmitted to the <a href="/articles/oval-window">oval window</a> of the <a href="/articles/cochlea">cochlea</a>.</p><h4>Anatomy</h4><p>The tympanic membrane is shaped like a flat cone pointing into the middle and inner ear. It consists of three layers:</p><ol>- +<p>The <strong>tympanic membrane</strong> is a thin membrane that separates the <a href="/articles/external-ear">external ear</a> from the <a href="/articles/middle-ear">middle ear</a>. It acts to transmit sound waves from air in the <a href="/articles/external-auditory-canal">external auditory canal</a> to the <a href="/articles/middle-ear-ossicles">ossicles</a> of the middle ear.</p><p>The <a href="/articles/malleus">malleus</a> is the first bone in the <a href="/articles/ossicular-chain">ossicular chain</a> that eventually sees the sound wave transmitted to the <a href="/articles/oval-window">oval window</a> of the <a href="/articles/cochlea">cochlea</a>.</p><h4>Gross anatomy</h4><p>The tympanic membrane is shaped like a flat cone pointing into the middle and inner ear. It consists of three layers:</p><ol>
-<a href="/articles/pars-tensa">pars tensa</a> : the tense portion of the membrane is the larger portion and extends from the anterior and posterior malleolar folds at the level of the lateral process of malleus to the inferior edge of the membrane</li>- +<a href="/articles/pars-tensa">pars tensa</a>: the tense portion of the membrane is the larger portion and extends from the anterior and posterior malleolar folds at the level of the lateral process of malleus to the inferior edge of the membrane</li>
-<a href="/articles/pars-flaccida">pars flaccida</a> : the flaccid portion of the membrane is much smaller and is the portion of the membrane above the anterior and posterior malleolar folds </li>- +<a href="/articles/pars-flaccida">pars flaccida</a>: the flaccid portion of the membrane is much smaller and is the portion of the membrane above the anterior and posterior malleolar folds </li>
-</ul><p>This is important because vessels and nerves (specifically <a href="/articles/chorda-tympani-nerve">chorda tympani nerve</a>) pass through the superior portion of the membrane. Additionally, the light reflex (cone of light) is specific to the anteroinferior portion of the membrane. Thus, when intervention is performed, the posteroinferior portion of the membrane is chosen. </p><h4><strong>Related pathology</strong></h4><ul>- +</ul><p>This is important because vessels and nerves (specifically <a href="/articles/chorda-tympani-nerve">chorda tympani nerve</a>) pass through the superior portion of the membrane. Additionally, the light reflex (cone of light) is specific to the anteroinferior portion of the membrane. Thus, when intervention is performed, the posteroinferior portion of the membrane is chosen. </p><h4>Related pathology</h4><ul>
-<a href="/articles/conductive-hearing-loss">conductive hearing loss</a> : secondary to rupture or perforation</li>-<li><a href="/articles/tympanic_membrane_retraction">tympanic membrane retraction</a></li>- +<a href="/articles/conductive-hearing-loss">conductive hearing loss</a>: secondary to rupture or perforation</li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/tympanic-membrane-retraction">tympanic membrane retraction</a></li>
Image 2 Diagram ( update )

Image 3 Diagram ( update )
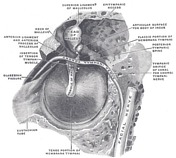
Image 4 Diagram ( update )







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.